Cannabis, a plant that has been used for both medical and recreational purposes for centuries, has become increasingly popular in recent decades. This is mainly because we're getting a better understanding of what compounds are in the plant and what they do. These compounds, called cannabinoids, play an important role in how cannabis affects the body. In this blog we explain what cannabinoids are, which types are found in cannabis and how they work together with the body to produce certain effects. So that you as a reader get the tools to consume in a conscious way.
What are cannabinoids?
But what are cannabinoids actually? It's a collection of compounds that interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in our body. This system helps regulate all kinds of processes, such as pain, mood, appetite and memory. There are three types of cannabinoids: endocannabinoids, phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are produced by the body itself, such as anandamide (AEA, also called the bliss molecule) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG, provides balance). Phytocannabinoids come from the cannabis plant and the best-known cannabinoids it contains are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Synthetic cannabinoids are made in laboratories for use in research and processing into medicines.
The main cannabinoids in cannabis
THC is the best-known cannabinoid because it gives you a high feeling. This happens because THC attaches to the CB1 receptors in the brain, changing your mood, appetite and pain perception. For example, you get the 'munchies' or become happier. THC can help with pain relief, nausea (especially in people receiving chemotherapy), muscle cramps and glaucoma, an eye disease. But it can also have negative side effects, for example you can become anxious or paranoid, or get a faster heart rate and memory problems.
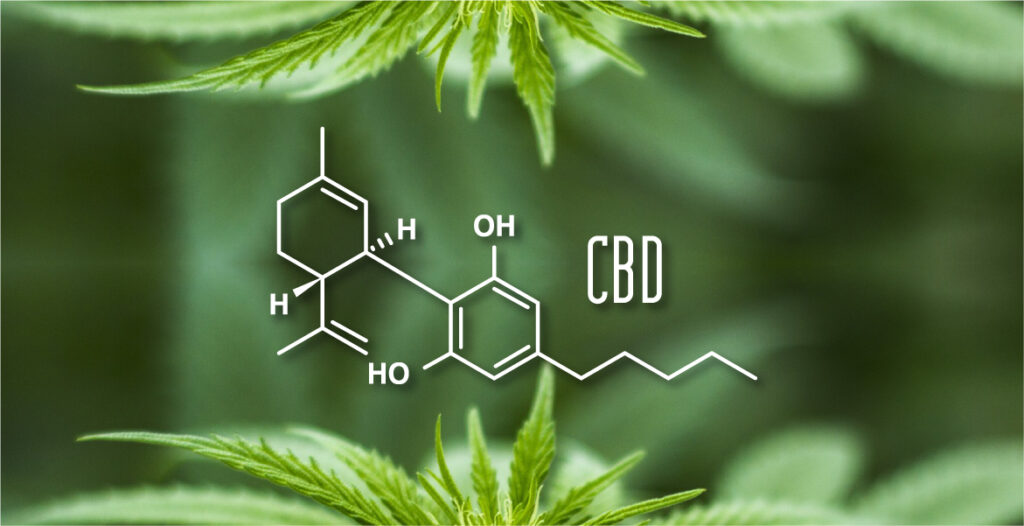
CBD works differently than THC, it doesn't make you high. Instead of directly binding to CB1 receptors, CBD influences the system in an indirect way. CBD inhibits the enzyme FAAH, which breaks down anandamide (AEA), a body's own substance that helps with relaxation, pain relief and mood. CBD ensures that anandamide stays active longer, which can make you feel calmer and more balanced. CBD also binds to other receptors, such as serotonin (5-HT1A), vanilloid (TRPV1) and PPAR receptors, which influence anxiety, pain, inflammation and cell repair. That's why CBD helps against stress, pain and inflammation. CBD also blocks some effects of THC, which can help against too strong a high and negative side effects like anxiety and paranoia. CBD is often used for epilepsy (such as Dravet syndrome), anxiety, chronic pain, inflammation and sleep problems. Possible side effects of CBD are fatigue, diarrhea and changes in appetite or weight.
CBN is formed when THC ages and breaks down through exposure to air and light. CBN is mildly psychoactive, but much less potent than THC. It's especially known for its calming effect and is therefore often used as a sleep aid. It can also help with pain and stimulating appetite. Possible side effects are drowsiness and dizziness.
CBG is the basis for other cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD. Because it usually occurs only in small amounts in cannabis, more and more research is being done on it. CBG has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. It could also help with glaucoma, because it lowers pressure in the eye. There are few known side effects of CBG, but it can interact with other medications.
CBC is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is often forgotten, but which can have medical benefits. CBC can help with pain relief, reducing inflammation and stimulating the growth of new brain cells. It also works together with other cannabinoids, making them work better. This is called the "entourage effect". There are few known side effects of CBC.
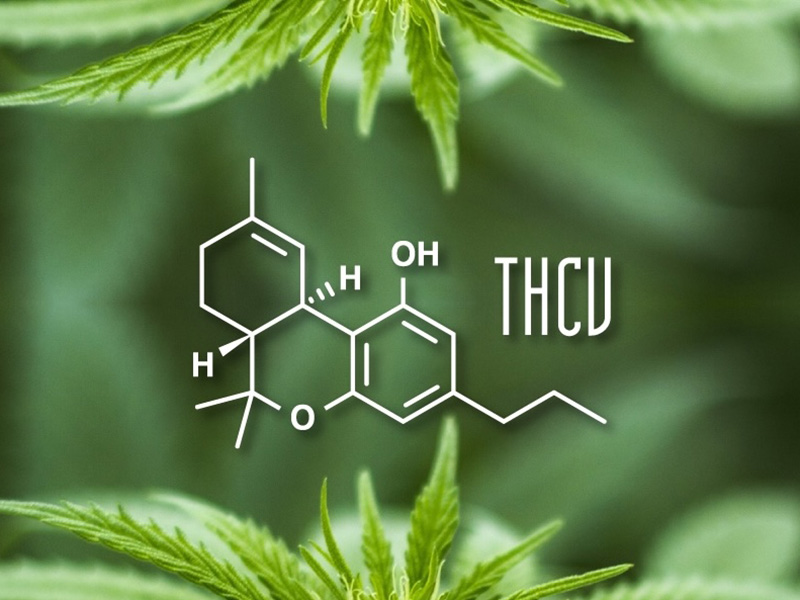
THCV is a lesser-known cannabinoid with special properties. It can suppress appetite, which can be useful for weight loss. It also has a positive effect on diabetes and epilepsy. In small amounts, THCV works as a CB1 inhibitor and reduces appetite. In higher doses, however, it can also give a high feeling, just like THC.
The Entourage Effect
One of the most interesting things about cannabinoids is how they work together to enhance their effect. This is called the "entourage effect". It means that cannabinoids and terpenes (the compounds that give cannabis its smell and taste) influence each other and work stronger together than on their own. For example, THC can relieve pain, but if there's also (enough) CBD present, the high becomes less intense and feels more balanced.
The endocannabinoid system has two important receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are mainly in the brain and nervous system and regulate things like pain, mood, appetite and memory. THC binds to these receptors, which causes the high and other effects. CB2 receptors are mainly in your immune system and organs and help with inflammation and immune responses. CBD mainly works on these receptors and therefore has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Future research and possible applications
Research into cannabinoids is still in full swing and there's still much to discover. Scientists are looking at possibilities such as brain protection, because some cannabinoids might help with diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Research is also being done on how cannabinoids can inhibit cancer and reduce the side effects of chemotherapy. Because they work anti-inflammatory, they could also be used for autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatism.

Responsible use of cannabis
While cannabis can have many benefits, it's important to use it responsibly. Always start with a low dose, especially if you're not used to cannabis yet, and increase it slowly to see how your body reacts. If you're sensitive to THC and don't like the feeling of being high, you can choose a product with more CBD, because this can reduce the effects of THC. It's also possible to smoke pure CBD or consume it in other ways. Consult with a doctor or specialist before using cannabis, especially if you take medications or have health problems.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids play a major role in how cannabis affects the body. By understanding how different types of cannabinoids work and how they interact with the endocannabinoid system, we get a better picture of their medical benefits. Whether it's pain management, reducing inflammation, relieving anxiety or protecting the brain, cannabinoids have many possibilities for future medical applications. But to properly utilize these benefits and minimize potential risks, responsible use and further research is essential.